Please feel free to download a white paper on the topic and the slides of our talk to the corresponding paper
Schultz, F.; Rettberg, T.; Spors, S. (2014): “On Spatial-Aliasing-Free Sound Field Reproduction using Infinite Line Source Arrays”. In Proc. of 136th Aud. Eng. Soc. Conv., Berlin. #9078.
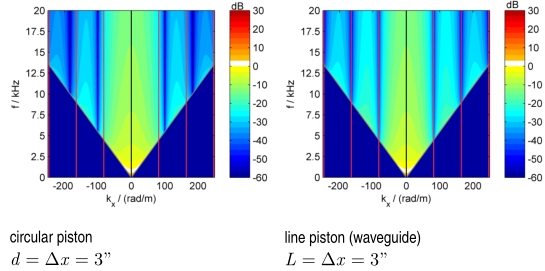
Abstract:
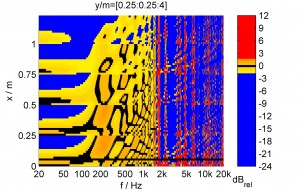
Concert sound reinforcement systems aim at the reproduction of homogeneous sound fields over extended audiences for the whole audio bandwidth. For the last two decades this has been mostly approached by using so called line source arrays due to their superior abilities of producing homogeneous sound fields. Design and setup criteria for line source arrays were derived as Wavefront Sculpture Technology in literature. This paper introduces a viewpoint on the problem at hand by utilizing a signal processing model for sound field synthesis. It will be shown that the optimal radiation of a line source array can be considered as a special case of spatial-aliasing-free synthesis of a wave front that propagates perpendicular to the array. For high frequencies the so called waveguide operates as a spatial lowpass filter and therefore attenuates energy that otherwise would lead to spatial aliasing artifacts.
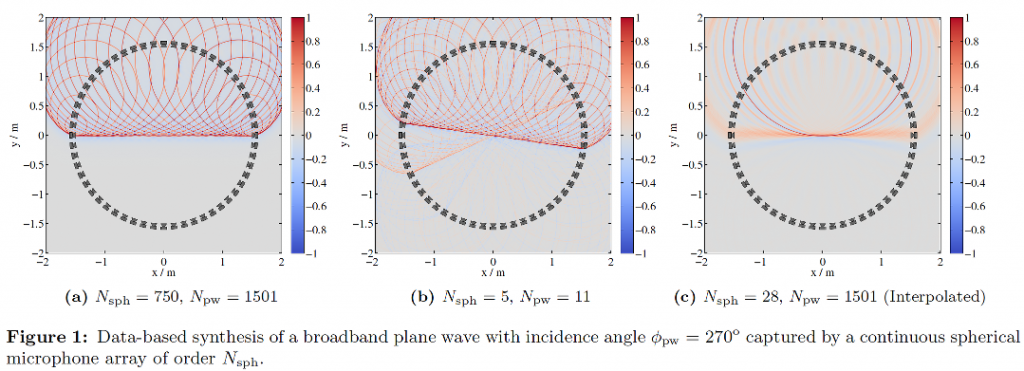
 An overview on the application of loudspeaker arrays for audio presentation is given. The foundations of Wave Field Synthesis and Higher-Order Ambisonics are introduced in an intutive manner. The possibilites and applications of Sound Field Synthesis techniques in comparison with conventional methods like Stereophony are highlighted.
An overview on the application of loudspeaker arrays for audio presentation is given. The foundations of Wave Field Synthesis and Higher-Order Ambisonics are introduced in an intutive manner. The possibilites and applications of Sound Field Synthesis techniques in comparison with conventional methods like Stereophony are highlighted.